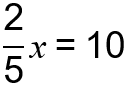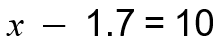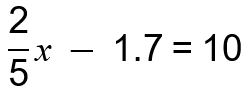To review the full Math-Grade 7 curriculum and see the online functionality, including ePub and assessment resources, please contact us to obtain login credentials.
The content that follows is what the teacher sees on the Lesson Overview page for each lesson in the teacher course.
Unit 2, Lesson 1: Modeling and Solving One-Variable, Two-Step Equations
Lesson Overview
Focusing Question: How can I model and solve a one-variable, two-step equation?
Learning Outcomes
- I can use concrete models to represent and solve an equation.
- I can use inverse operations and properties of algebra to solve an equation.
- I can locate the solution to an equation on a number line.
| Texas Essential Knowledge and Skills (TEKS) |
| 7.10B Expressions, equations, and relationships. The student applies mathematical process standards to use one-variable equations and inequalities to represent situations. The student is expected to represent solutions for one-variable, two-step equations and inequalities on number lines. |
| 7.11A Expressions, equations, and relationships. The student applies mathematical process standards to solve one-variable equations and inequalities. The student is expected to model and solve one-variable, two-step equations and inequalities. |
| 7.1C Mathematical process standards. The student uses mathematical processes to acquire and demonstrate mathematical understanding. The student is expected to select tools, including real objects, manipulatives, paper and pencil, and technology as appropriate, and techniques, including mental math, estimation, and number sense as appropriate, to solve problems. |
| English Language Proficiency Standards (ELPS) |
| 2.D Cross-curricular second language acquisition/listening. The ELL listens to a variety of speakers including teachers, peers, and electronic media to gain an increasing level of comprehension of newly acquired language in all content areas. ELLs may be at the beginning, intermediate, advanced, or advanced high stage of English language acquisition in listening. In order for the ELL to meet grade-level learning expectations across the foundation and enrichment curriculum, all instruction delivered in English must be linguistically accommodated (communicated, sequenced, and scaffolded) commensurate with the student’s level of English language proficiency. The student is expected to monitor understanding of spoken language during classroom instruction and interactions and seek clarification as needed. |
Overview of Process Standard(s)
In this lesson, select tools such as algebra tiles, technology, or pencil and paper and techniques such as standard algorithms, properties of algebra, and mental math, to model and solve one-variable, two-step equations. Students may:
- Use algebra tiles to represent an equation and connect their actions with the tiles to inverse operations performed on variables an constants.
- Use technology to generate graphs and tables to show values of the variable that make the equation true.
- Use mental math to perform operations on whole number or integer coefficients and constants.
Prior Learning Supports
In 6th grade, students solved one-variable, one-step equations and inequalities and then represented the solutions on number lines. By “one-step,” we mean that one arithmetic operation is being performed on the variable, such as multiplication or subtraction.
In 7th grade, students extend this understanding to solving two-step equations and inequalities where there are two operations being performed on the variable that must be undone in order to solve the equation.
Lesson Plan
See the subsections below for lesson components and guidance for instruction.
- Exploration
- Play the instructional video to launch instruction.
- Guide students through the activity.
- Provide students with the Blackline Master of the Student Pages or assign the Google Slides as appropriate.
- Use the Answer Key as necessary.
- Explanation
- Assign students the ePub to provide direct instruction on the content along with guided practice through examples and a set of practice questions.
- Performance Task
- As a formative assessment, use the performance task to determine what students know about the topic.
- Performance tasks have four versions: on-level, simplified, enriched, and scaffolded.
- Allow students to work in pairs or small groups if desired.
- If there are multiple performance tasks, select one or encourage self differentiation by allowing students to select a task based on their interests and comfort levels.
Lesson Components
| Exploration | Explanation | Performance Task |
|---|---|---|
 Instructional Video Instructional Video Blackline Master (Student Page) Blackline Master (Student Page) Blackline Master (AK) Blackline Master (AK) Google Slides Google Slides |  ePub: Solving Two-Step Equations ePub: Solving Two-Step Equations |  7.11A Performance Task- Picture Puzzle 7.11A Performance Task- Picture Puzzle |
Pacing Guide
- Exploration (20-25 minutes)
- Explanation and Practice (20-25 minutes)
- Performance Task (30-35 minutes)
Teaching Hints
- A concrete model such as algebra tiles or cups and counters allows students to make connections between the actions they take with the variable or constant and the property of operations that justifies those actions.
- Solving equations symbolically makes routine use of the additive inverse and multiplicative inverse properties. Make that application explicit.
Teacher Materials
- Algebra tiles
- Cups and counters (e.g., centimeter cubes or beans) for demonstration
Student Materials
- Pencil
- Paper
- Algebra tiles
- Cups
- Counters (centimeter cubes or beans)
Vocabulary
One way to support students’ acquisition of new vocabulary terms is to preteach the vocabulary terms using a strategy such as a Frayer model. For these key terms, we provide partially completed Frayer models to which students should add as they move through the lesson and develop a deeper understanding of the vocabulary term. Click on the term to see the Frayer model.
Use this template for additional vocabulary words.